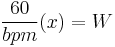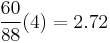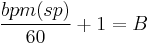Film score
A film score (also sometimes called background music or incidental music) is original music written specifically to accompany a film, forming part of the film's soundtrack, which also usually includes dialogue and sound effects. The score comprises a number of orchestral, instrumental or choral pieces called cues which are timed to begin and end at specific points during the film in order to enhance the dramatic narrative and the emotional impact of the scene in question.[1]
Songs are usually not considered part of the film's score,[2] although songs do also form part of the film's soundtrack. Although some songs, especially in musicals, are based on thematic ideas from the score (or vice-versa), scores usually do not have lyrics, except for when sung by choirs or soloists as part of a cue. Similarly, pop songs which are "needle dropped" into a specific scene in film for added emphasis are not considered part of the score, although occasionally the score's composer will write an original pop song based on his themes, such as James Horner's "My Heart Will Go On" from Titanic, written for Celine Dion.
Scores are written by one or more composers, under the guidance of the film's director and/or producer, and are then usually performed by an ensemble of musicians - most often comprising an orchestra or band, instrumental soloists, and choir or vocalists - and recorded by a sound engineer.
Film scores encompass an enormous variety of styles of music, depending on the nature of the films they accompany. The majority of scores are orchestral works rooted in Western classical music, but a great number of scores also draw influence from jazz, rock, pop, blues, New Age ambient music, and a wide range of ethnic and world music styles. Since the 1950s, a growing number of scores have also included electronic elements as part of the score, and many scores written today feature a hybrid of orchestral and electronic instruments.[3]
Since the invention of digital technology and audio sampling, many low budget films have been able to rely on digital samples to imitate the sound of live instruments, and many scores are created and performed wholly by the composers themselves, by programming sophisticated music composition software.
Contents |
Process of creation
Spotting
The composer usually enters the creative process towards the end of filming, at around the same time as the film is being edited, although on some occasions the composer is on hand during the entire film shoot, especially when actors are required to perform with or be aware of original diegetic music. The composer is shown an unpolished "rough cut" of the film, before the editing is completed, and talks to the director or producer about what sort of music is required for the film in terms of style and tone. The director and composer will watch the entire film, taking note of which scenes require original music. During this process the composer will take precise timing notes so that he or she knows how long each cue needs to last, where it begins, where it ends, and of particular moments during a scene with which the music may need to coincide in a specific way. This process is known as "spotting".[4]
Occasionally, a film maker will actually edit his film to fit the flow of music, rather than the other way around, which is the norm. Director Godfrey Reggio edited his films Koyaanisqatsi and Powaqqatsi based on composer Philip Glass's music.[5] Similarly, the relationship between director Sergio Leone and composer Ennio Morricone was such that the finale of The Good, the Bad and the Ugly[6] and the films Once Upon a Time in the West and Once Upon a Time in America were edited to Morricone's score as the composer had prepared it months before the film's production ended. Also, the finale of Steven Spielberg's E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial was edited to match the music of his long-time collaborator John Williams: as recounted in a companion documentary on the DVD, Spielberg gave Williams complete freedom with the music and asked him to record the cue without picture; Spielberg then re-edited the scene later to match the music.
Less frequently, a composer will be asked to write music based on his or her impressions of the script or storyboards, without seeing the film itself, and is given more freedom to create music without the need to adhere to specific cue lengths or mirror the emotional arc of a particular scene. This approach is usually taken by a director who does not wish to have the music comment specifically on a particular scene or nuance of a film, and which can instead be inserted into the film at any point the director wishes during the post-production process. Composer Hans Zimmer was asked to write music in this way in 2010 for director Christopher Nolan's film Inception;[7] composer Gustavo Santaolalla did the same thing when he wrote his Oscar-winning score for Brokeback Mountain.[8]
Syncing
When writing music for film, one goal is to sync dramatic events happening on screen with musical events in the score. There are many different methods for syncing music to picture. These include using sequencing software to calculate timings, using mathematic formulas and free timing with reference timings. Composers work using SMPTE timecode for syncing purposes.[9]
When syncing music to picture, generally a leeway of 3-4 frames late or early allows the composer to be extremely accurate. Using a technique called Free Timing, a conductor will use either (a) a stop watch or studio size stopclock, or (b) watch the film on a screen or video monitor while conducting the musicians to predetermined timings. There are represented visually by vertical lines (streamers) and bursts of light called punches. These are put on the film by the Music Editor at points specified by the composer. In both instances the timings on the clock or lines scribed on the film have corresponding timings which are also at specific points (beats) in the composer/conductor score.
Digital Sequencer
Using a digital sequencer such as Digital Performer, Logic, or Cubase, composers are able to sync music to picture with extreme accuracy using SMPTE timecode. Outlined below is one method using Digital Performer[10]:
- Import the video to score into Digital Performer
- Place a marker in the sequencer timeline where you wish to "hit" the event in the scene with music.
- Note the SMPTE timecode (i.e. 01:00:15:23)
- Note the start and end measure (bars+beats), and set it to an exact beat.
- If the "end time" (timecode) field is greyed out, click the options button to open it up.
- Enter the timecode where the downbeat will hit in the "end time" field.
You now will have synchronized an event in the film with a musical event, in time.
Written Click Track
A written click track is a method of writing bars of music in consistent time values (i.e. 4 beats in :02⅔ seconds) to establish a constant tempo in lieu of a metronome value (i.e. 88 Bpm). A composer would use a written click if they planned to conduct live performers. When using other methods such as a metronome, the conductor has a perfectly spaced click playing in his ear which he conducts to. This can yield stiff and lifeless performances in slower more expressive cues. You can convert a standard BPM value to a written click where X represents the number of beats per bar, and W represents time in seconds, by using the following equation:
Written clicks are expressed using 1/3 second increments, so the next step is to round the decimal to either 0, 1/3, or 2/3 of a second. The following is an example for 88 BPM:
2.72 rounds to 2.66, so the written click is 4 beats in :02⅔ seconds.
Once the composer has identified the location in the film they wish to sync with musically, they must determine the musical beat this event occurs on. To find this, they use the following equation, where bpm is beats per minute, sp is the sync point in real-time (i.e. 33.7 seconds), and B is the beat number in 1/3 increments (i.e. 49⅔).
Writing
Once the spotting session has been completed and the precise timings of each cue determined, the composer will then work on writing the score. The methods of writing the score vary from composer to composer; some composers prefer to work with a traditional pencil and paper, writing notes by hand on a staff and performing works-in-progress for the director on a piano, while other composers write on computers using sophisticated music composition software such as Digital Performer, Logic Pro, Cubase or Protools.[11] Working with software allows composers to create MIDI-based demos of cues, called MIDI mockups, for review by the filmmaker prior to the final orchestral recording.
The length of time a composer has to write the score varies from project to project; depending on the post-production schedule, a composer may have as little as two weeks, or as much as three months to write the score. In normal circumstances, the actual writing process usually lasts around six weeks from beginning to end.
The actual musical content of a film score is wholly dependent on the type of film being scored, and the emotions the director wishes the music to convey. A film score can encompass literally thousands of different combinations of instruments, ranging from full symphony orchestral ensembles to single solo instruments to rock bands to jazz combos, along with a multitude of ethnic and world music influences, soloists, vocalists, choirs and electronic textures. The style of the music being written also varies massively from project to project, and can be influenced by the time period in which the film is set, the geographic location of the film's action, and even the musical tastes of the characters. As part of their preparations for writing the score the composer will often research different musical techniques and genres as appropriate for that specific project; as such, it is not uncommon for established film composers to be proficient at writing music in dozens of different styles.
Orchestration
Once the music has been written, it must then be arranged or orchestrated in order for the ensemble to be able to perform it. The nature and level of orchestration varies from project to project and composer to composer, but in its basic form the orchestrator's job is to take the single-line music written by the composer and "flesh it out" in to instrument-specific sheet music for each member of the orchestra to perform.
Some composers, notably Ennio Morricone, orchestrate their own scores themselves, without using an additional orchestrator. Some composers provide intricate details in how they want this to be accomplished, and will provide the orchestrator with copious notes outlining which instruments are being asked to perform which notes, giving the orchestrator no personal creative input whatsoever beyond re-notating the music on different sheets of paper as appropriate. Other composers are less detailed, and will often ask orchestrators to "fill in the blanks", providing their own creative input into the makeup of the ensemble, ensuring that each instrument is capable of performing the music as written, and even allowing then to introduce performance techniques and flourishes to enhance the score.
Over the years several orchestrators have become linked to the work of one particular composer, often to the point where one will not work without the other. Examples of enduring composer-orchestrator relationships include Jerry Goldsmith with Arthur Morton, Alexander Courage and Herbert W. Spencer; Miklos Rozsa with Eugene Zador; Alfred Newman with Edward Powell, Ken Darby and Hugo Friedhofer; Danny Elfman with Steve Bartek; David Arnold with Nicholas Dodd; Basil Poledouris with Greig McRitchie; and Elliot Goldenthal with Robert Elhai. Others have become orchestrators-for-hire, and work with many different composers over the course of their careers; examples of prominent film music orchestrators include Pete Anthony, Jeff Atmajian, Brad Dechter, Bruce Fowler, John Neufeld, Thomas Pasatieri, Conrad Pope, Nic Raine and J.A.C. Redford.
Once the orchestration process has been completed, the sheet music is physically printed onto paper by one or more music copyists, and is ready for performance.
Recording
When the music has been composed and orchestrated, the orchestra or ensemble then performs it, often with the composer conducting. Musicians for these ensembles are often uncredited in the film or on the album and are contracted individually (and if so, the orchestra contractor is credited in the film or the soundtrack album). However, some films have recently begun crediting the contracted musicians on the albums under the name Hollywood Studio Symphony after an agreement with the American Federation of Musicians. Other performing ensembles that are often employed include the London Symphony Orchestra (performing film music since 1935)[12] the City of Prague Philharmonic Orchestra (an orchestra dedicated exclusively to recording), and the Northwest Sinfonia.
The orchestra performs in front of a large screen depicting the movie, and sometimes to a series of clicks called a "click-track" that changes with meter and tempo, assisting the conductor to synchronize the music with the film.[13]
More rarely, the director will talk to the composer before shooting has started, so as to give more time to the composer or because the director needs to shoot scenes (namely song or dance scenes) according to the final score. Sometimes the director will have edited the film using "temp (temporary) music": already published pieces with a character that the director believes to fit specific scenes.
Elements of a film score
Temp tracks
In some instances, film composers have been asked by the director to imitate a specific composer or style present in the temp track.[14] On other occasions, directors have become so attached to the temp score that they decide to use it and reject the original score written by the film composer. One of the most famous cases is Stanley Kubrick's 2001: A Space Odyssey, where Kubrick opted for existing recordings of classical works, including pieces by composer György Ligeti rather than the score by Alex North,[15] although Kubrick had also hired Frank Cordell to do a score. While North's 2001 is indeed a major example, it is not the sole case of well-known rejected scores. Others include Torn Curtain (Bernard Herrmann),[16] Troy (Gabriel Yared),[17] Peter Jackson's King Kong (Howard Shore)[18] and The Bourne Identity (Carter Burwell).[19]
Structure
Films often have different themes for important characters, events, ideas or objects, an idea often associated with Wagner's use of leitmotif.[20] These may be played in different variations depending on the situation they represent, scattered amongst incidental music. An example of this technique is John Williams' score for the Star Wars saga, and the numerous themes associated with characters like Darth Vader, Luke Skywalker, and Princess Leia Organa (see Star Wars music for more details). Other examples are Italian composers Stefano Lentini and oscar's winner Ennio Morricone.[21] The Lord of the Rings trilogy uses a similar technique, with recurring themes for many main characters and places. Others are less known by casual moviegoers, but well known among score enthusiasts, such as Jerry Goldsmith's underlying theme for the Borg in Star Trek: First Contact, or his Klingon theme from Star Trek: The Motion Picture which other composers carry over into their Klingon motifs, and he has brought back on numerous occasions as the theme for Worf, Star Trek: The Next Generation's most prominent Klingon. Michael Giacchino employed character themes in the soundtrack for the 2009 animated film Up, for which he received the Academy Award for Best Score. His orchestral soundtrack for the television series Lost also depended heavily on character and situation-specific themes.
In 1983, a non-profit organization, the Society for the Preservation of Film Music, was formed to preserve the "byproducts" of creating a film score:[22] the music manuscripts (written music) and other documents and studio recordings generated in the process of composing and recording scores which, in some instances, have been discarded by the movie studios. The written music must be kept to perform the music on concert programs and to make new recordings of it. Sometimes only after decades has an archival recording of a film score been released on CD.
Source music
Most films have between 40 and 120 minutes of music. However, some films have very little or no music; others may feature a score that plays almost continuously throughout. Dogme 95 is a genre that has music only from sources within a film, such as from a radio or television. This is called "source music" (or a "source cue") because it comes from an on screen source that can actually be seen or that can be inferred (in academic film theory such music is called "diegetic" music, as it emanates from the "diegesis" or "story world").[23] An example of "source music" is the use of the Frankie Valli song "Can't Take My Eyes Off You" in Michael Cimino's "The Deer Hunter". Alfred Hitchcock's 1963 thriller The Birds is an example of a Hollywood film with no non-diegetic music whatsoever.
Brief History
Origins
Before the age of recorded sound in motion pictures, efforts were taken to provide suitable music for films, usually through the services of an in-house pianist or organist, and, in some cases, entire orchestras, typically given cue sheets as a guide. A pianist was present to perform at the Lumiere brother's first film screening in 1895.[24] In 1914, The Oz Film Manufacturing Company sent full-length scores by Louis F. Gottschalk for their films. Other examples of this include Victor Herbert's score in 1915 to The Fall of a Nation (a sequel to The Birth of a Nation) and Camille Saint-Saëns' music for The Assassination of the Duke of Guise in 1908. It was preceded by Nathaniel D. Mann's score for The Fairylogue and Radio-Plays by four months, but that was a mixture of interrelated stage and film performance in the tradition of old magic lantern shows.[25] Most accompaniments at this time, these examples notwithstanding, comprised pieces by famous composers, also including studies. These were often used to form catalogues of photoplay music, which had different subsections broken down by 'mood' and/or genre: dark, sad, suspense, action, chase, etc.
The rise of the 'film score'
German cinema, which was highly influential in the era of silent movies, provided some original scores such as Fritz Lang's movies Die Nibelungen (1924) and Metropolis (1927) which were accompanied by original full scale orchestral and leitmotific scores written by Gottfried Huppertz, who also wrote piano-versions of his music, for playing in smaller cinemas. Friedrich W. Murnau's movies Nosferatu (1922 - music by Hans Erdmann) and Faust – eine deutsche Volkssage (1926 - music by Werner Richard Heymann) also had original scores written for them. Other films like Murnau's Der letzte Mann contained a mixing of original compositions (in this case by Giuseppe Becce) and library music / folk tunes, which were artistically included into the score by the composer.
The arrival of sound
When sound came to movies, director Fritz Lang barely used musical scores in his movies anymore. Apart from Peter Lorre whistling a short piece from Edvard Grieg's Peer Gynt, Lang's movie M - Eine Stadt sucht einen Mörder was lacking musical accompaniment completely and Das Testament des Dr. Mabuse only included one original piece written for the movie by Hans Erdmann played at the very beginning and end of the movie. One of the rare occasions on which music occurs in the movie is a song one of the characters sings, that Lang uses to put emphasis on the man's insanity, similar to the use of the whistling in M.
1940s to Present
Though "the scoring of narrative features during the 1940s lagged decades behind technical innovations in the field of concert music,"[26] the 1950s saw the rise of the modernist film score. Director Elia Kazan was open to the idea of jazz influences and dissonant scoring and worked with Alex North, whose score for A Streetcar Named Desire (1951) combined dissonance with elements of blues and jazz. Kazan also approached Leonard Bernstein to score On the Waterfront (1954) and the result was reminiscent of earlier works by Aaron Copland and Igor Stravinsky with its "jazz-based harmonies and exciting additive rhythms."[26] A year later, Leonard Rosenman, inspired by Arnold Schoenberg, experimented with atonality in his scores for East of Eden (1955) and Rebel Without a Cause (1955). In his ten-year collaboration with Alfred Hitchcock, Bernard Herrmann experimented with ideas in Vertigo (1958), Psycho (1960), and The Birds (1963). The use of non-diegetic jazz was another modernist innovation, such as jazz star Duke Ellington's score for Otto Preminger's Anatomy of a Murder (1959).
A full film score widely regarded as the first made by a popular artist came in 1973 with the film Pat Garret and Billy the Kid, by Bob Dylan. However the album received very little critical acclaim. This had not been done before in popular film history as featured bands had films written around their music such as in the animation Yellow Submarine with music by The Beatles.
Composers
Academy Award nominees and winners
The following list includes all composers who have been nominated for an Academy Award by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences in the Best Original Score category (which, over the years, had gone by a variety of names, included song scores and arrangements, and been split into awards for scoring in dramas and comedies). Winners of the Award appear in bold. Note: Composers whose only Oscar nominations came in the Best Original Song category are not listed, and Best Original Song wins are not counted in the wins tally.
Source: The Official Academy Awards Database [1]
Other award nominees and winners
The following list includes all composers who have been nominated for one of the other major film music awards (Golden Globes, BAFTA Awards, Grammy Awards, Emmy Awards, International Film Music Critics Association), but have never been nominated for an Oscar. Winners of an Award appear in bold.
|
|
|
Sources: HFPA Award Search [2], BAFTA Awards Database [3], Primetime Emmy Award Database [4], Grammy Awards Archive [5], IFMCA Awards Archive [6]
Box office champions
The following list includes all composers who have scored one of the 100 Highest Grossing Films of All Time, but have never been nominated for a major award (Oscar, Golden Globe etc.)
- William Alwyn – Swiss Family Robinson (1960)
- David Buttolph – House of Wax (1953)
- George S. Clinton – Austin Powers in Goldmember (2002)
- Brad Fiedel – Terminator 2: Judgment Day (1991)
- Alexander Janko – My Big Fat Greek Wedding (2002)
- Bill Justis – Smokey and the Bandit (1977)
- Harald Kloser – The Day After Tomorrow (2004), 2012 (2009)
- Mark Mancina – Twister (1996)
- Heitor Pereira – Despicable Me (2010), The Smurfs (2011)
- Trevor Rabin – Armageddon (1998), National Treasure: Book of Secrets (2007)
- William Ross – Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets (2002)
- Pharrell Williams – Despicable Me (2010)
- Chris Wilson – My Big Fat Greek Wedding (2002)
Source: Box Office Mojo – All-Time Domestic Box Office Grosses [7], All-Time Domestic Box Office Grosses Adjusted for Inflation [8], All-Time Worldwide Box Office Grosses [9]
Production music
Many companies such as Jingle Punks, Associated Production Music and Extreme Music provide music to various film, TV and commercial projects for a fee. Sometimes called library music, the music is owned by production music libraries and licensed to customers for use in film, television, radio and other media. Unlike popular and classical music publishers, who typically own less than 50 percent of the copyright in a composition, music production libraries own all of the copyrights of their music, meaning that it can be licensed without seeking the composer's permission, as is necessary in licensing music from normal publishers. This is because virtually all music created for music libraries is done on a work for hire basis. Production music is therefore a very convenient medium for media producers — they can be assured that they will be able to license any piece of music in the library at a reasonable rate.
Production music libraries will typically offer a broad range of musical styles and genres, enabling producers and editors to find much of what they need in the same library. Music libraries vary in size from a few hundred tracks up to many thousands. The first production music library was setup by De Wolfe in 1927 with the advent of sound in film, the company originally scored music for use in silent film.[27] Another music library was set up by Ralph Hawkes of Boosey & Hawkes Music Publishers in the 1930s.[28] APM, the largest US library, has over 250,000 tracks.[29]
See also
- AFI's 100 Years of Film Scores
- Filmi, Bollywood film music
- List of film score composers
- Musivisual Language
Film music organizations
- ASCAP - Performing rights organization
- BMI - Performing rights organization
- Film Musicians Secondary Markets Fund
- Society of Composers and Lyricists
Film music review sites
Independent specialist original soundtrack recording labels
- 1M1 Records
- Digitmovies AE
- Film Score Monthly
- Intrada Records
- La-La Land Records
- Milan Records
- MovieScore Media
- Perseverance Records
- Prometheus Records
- Trunk Records
- Varèse Sarabande
Journals
References
- ^ Savage, Mark. "Where Are the New Movie Themes?" BBC, 28 July 2008.
- ^ Rockwell, John (21 May 1978). "When the Soundtrack Makes the Film". The New York Times. http://select.nytimes.com/gst/abstract.html?res=F30617F8355A11728DDDA80A94DD405B888BF1D3&scp=4&sq=film%20soundtrack&st=cse. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Bebe Barron: Co-composer of the first electronic film score, for 'Forbidden Planet'". The Independent (London). 8 May 2008. http://www.independent.co.uk/news/obituaries/bebe-barron-cocomposer-of-the-first-electronic-film-score-for-forbidden-planet-822755.html. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- ^ Film scoring
- ^ The Creators
- ^ SoundtrackNet: The Good, The Bad and The Ugly Soundtrack
- ^ We Built Our Own World: Hans Zimmer and the Music of 'Inception'
- ^ TIMBT: Gustavo Santolalla interview
- ^ SMPTE
- ^ MOTU.com - Overview
- ^ Kompanek, Sonny. From Score To Screen: Sequencers, Scores And Second Thoughts: The New Film Scoring Process. Schirmer Trade Books, 2004. ISBN 978-0825673085
- ^ London Symphony Orchestra and Film Music LSO. Retrieved 30 June 2011
- ^ Home Recording Glossary: Click Track
- ^ George Burt, The art of film music, Northeastern University Press
- ^ 2001 A Space Odyssey - Original soundtrack by Alex North, commissioned but unused by Stanley Kubrick, conducted by Jerry Goldsmith
- ^ SoundtrackNet: Torn Curtain Soundtrack
- ^ SoundtrackNet: Article - Gabriel Yared's Troy
- ^ Music on Film:: News:: Article in Variety about James Newton Howard's King Kong score
- ^ The Bourne Identity
- ^ leitmotif - Definition from the Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary
- ^ Star Wars and Wagner's Ring
- ^ About The Film Music Society
- ^ The Functions of Film Music
- ^ Film music: a history By James Eugene Wierzbicki, p.20
- ^ Fairylogue was released 24 September 1908; Assassinat was released 17 November 1908
- ^ a b Cooke, Mervyn (2008). A History of Film Music. New York: Cambridge University Press.
- ^ De Wolfe, Warren (1988). de wolfe millennium catalogue. London: De Wolfe Music.
- ^ Wallace, Helen (2007). Boosey & Hawkes The Publishing Story. London: B&H London. ISBN 9780851625140.
- ^ "PRWeb July 2007". http://www.prweb.com/releases/2007/07/prweb539516.htm. Retrieved 2007-07-20.
Further reading
- Andersen, Martin Stig. “Electroacoustic Sound and Audiovisual Structure in Film.” eContact! 12.4 — Perspectives on the Electroacoustic Work / Perspectives sur l’œuvre électroacoustique (August 2010). Montréal: CEC.
- Elal, Sammy and Kristian Dupont (Eds.). “The Essentials of Scoring Film.” Minimum Noise. Copenhagen, Denmark.
- Various contributors [wiki]. “Films with Significant Electroacoustic Content.” eContact! 8.4 — Ressources éducatives / Educational Resources (September 2006). Montréal: CEC.
External links
- Film music organizations
- Film music review sites
- Cinemusic (cinemusic.net)
- MusicWeb International: Film Music on the Web (site closed in December 2006 and remains for archive purposes only)
- MainTitles (maintitles.net)
- Movie Music UK (moviemusicuk.us)
- Movie Wave (movie-wave.net )
- ScoreNotes (scorenotes.com)
- Journals (online and print)
- Film Music Magazine
- Film Music Review
- The Journal of Film Music
- (French) UnderScores : le magazine de la musique de film
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||